- 22 Jul 2024
- 2 Minutes to read
Jet fire
- Updated on 22 Jul 2024
- 2 Minutes to read
What is a Jet Fire?
A Jet Fire is defined as a turbulent dispersion fire resulting from the combustion of a flammable material continuously released from equipment with high momentum in a particular direction. One of the most important characteristics of a Jet Fire is the high momentum of the released material from its equipment. The footage below from Gexcon's Fire and Explosion Testing facility shows the direct ignition of a flammable gas released at high pressure due to an ignition source close to the release point.
How does a Jet Fire arise?
Jet Fires can occur after mechanical damage or damage due to excessive overpressure to process equipment such as a broken pipe, a flange, or a relief valve, in which a gas or a liquefied gas is stored or is being transported under pressure. The ignition is mostly spontaneous, caused by the friction of the leaking material against the edge of the hole. Jet Fires can fully develop in an unconfined environment. The released material state can be a gas, a flashing liquid (two-phase) or a pure liquid. A Jet Fire typically occurs for substances such as hydrogen, or light hydrocarbons (e.g., natural gas, propane, etc.).
The danger from a Jet Fire arises from the heat radiation's effect on the environment. The determination of the effects of a Jet Fire requires the prediction of the Jet Fire size and thermal flux as a function of distance. The calculation of the thermal flux density from the flame in the case of a Jet Fire requires knowledge of the physical and chemical properties of the combustible material, release conditions of the material from pressurised equipment, and the weather conditions at the place of origin of the Jet Fire (e.g., temperature, relative humidity, wind speed, etc.) (Bosch, 2005).
Characteristics of a Jet Fire
The shape of the Jet Fire can be defined as the envelope of the visible flame after the influence of wind is disregarded. This characteristic flame shape can be determined by the length of the jet and its diameter. More complex approaches for describing the Jet Fire flame and heat flux from jet flames require the use of models which can be implemented into consequence modelling tools for instance, integral model-based tol EFFECTS or CFD-based modelling software FLACS.
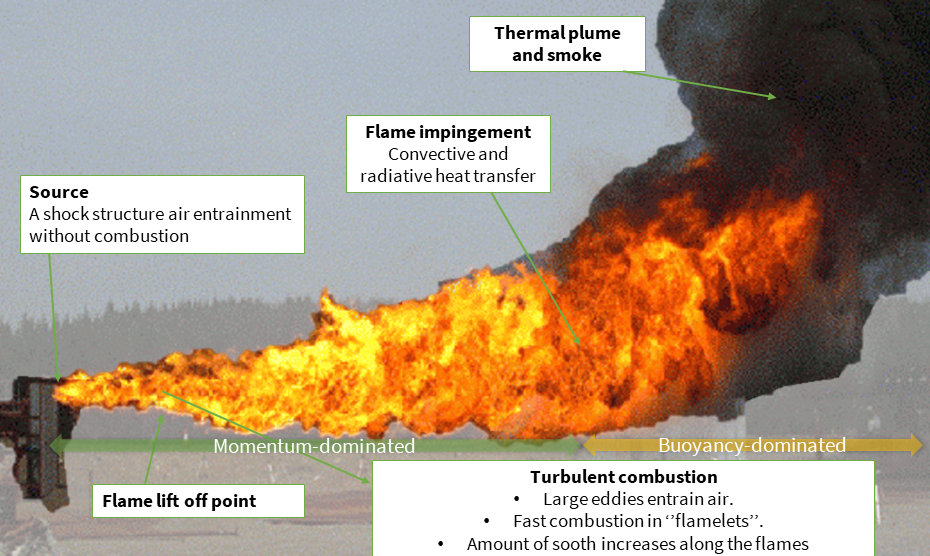
If a Jet Fire occurs in a relatively compact installation, the equipment may come in direct contact with flames, particularly, flame impingement, and subsequently fail causing a domino effect.
References
Bosch, C. v. (2005). Methods for the calculation of physical effects 'Yellow book' CPR 14E. The Hague: Ministerie van Verkeer en Waterstaat.

