- 19 Jul 2024
- 3 Minutes to read
How to create a mixture
- Updated on 19 Jul 2024
- 3 Minutes to read
EFFECTS and RISKCURVES allow the possibility of defining mixtures. Creating a mixture in the chemical database can be done in two ways:
Editing an already existing sample mixture.
Creating a new mixture from scratch.
Both methods use mixing rules such as ideal mixing, Le Chatelier, and Kendal-Monroe for the calculation of mixture properties.
Points to remember when creating mixtures
As explained in the article "Chemical database" there are a few limitations when creating mixtures that need to be taken into account, such as binary interactions, chemical reactions, absorption and solubility effects not being considered when calculating mixture properties.
Method 1: Editing an existing sample mixture
The first way to create a new user-defined mixture is to edit the composition of an already-existing mixture. To do this, follow the steps below:
Filter for sample mixture
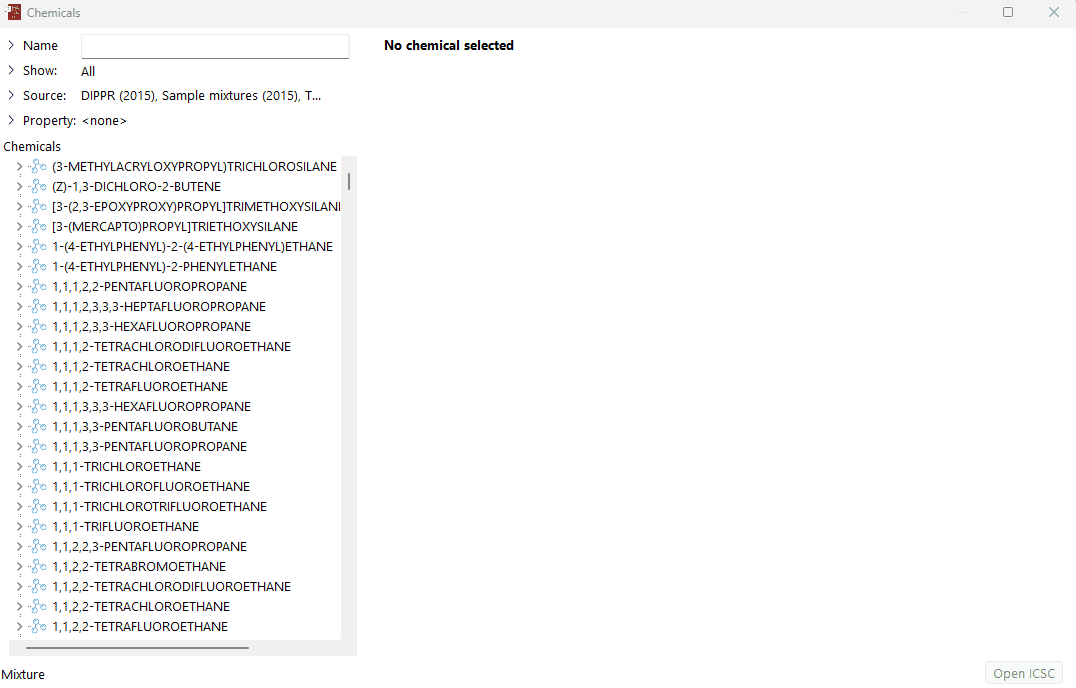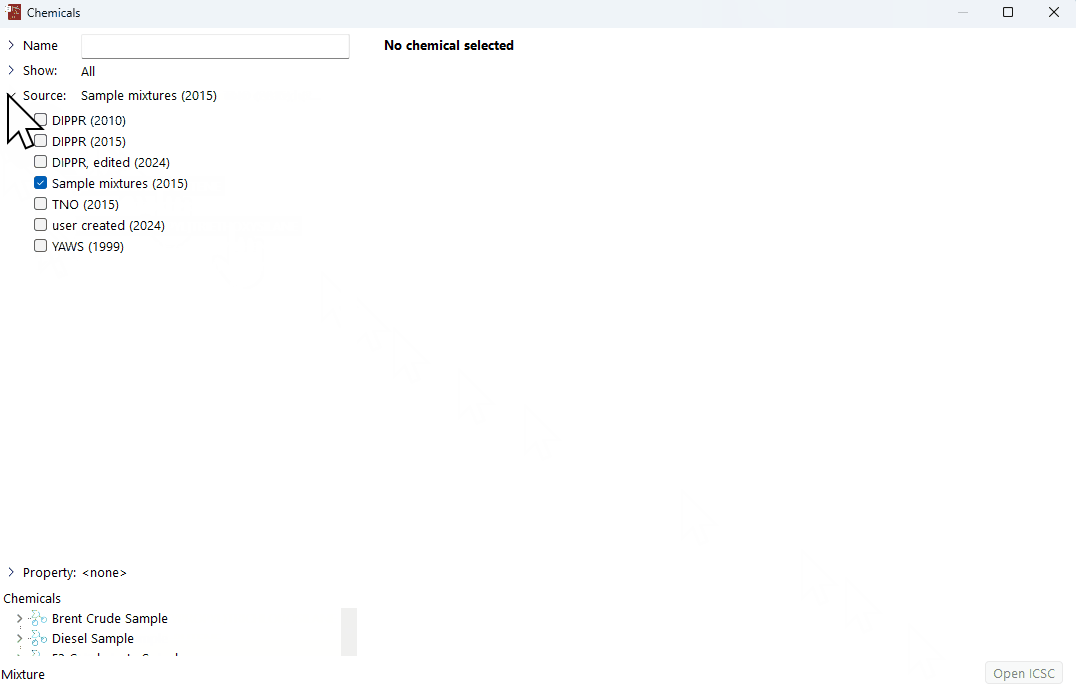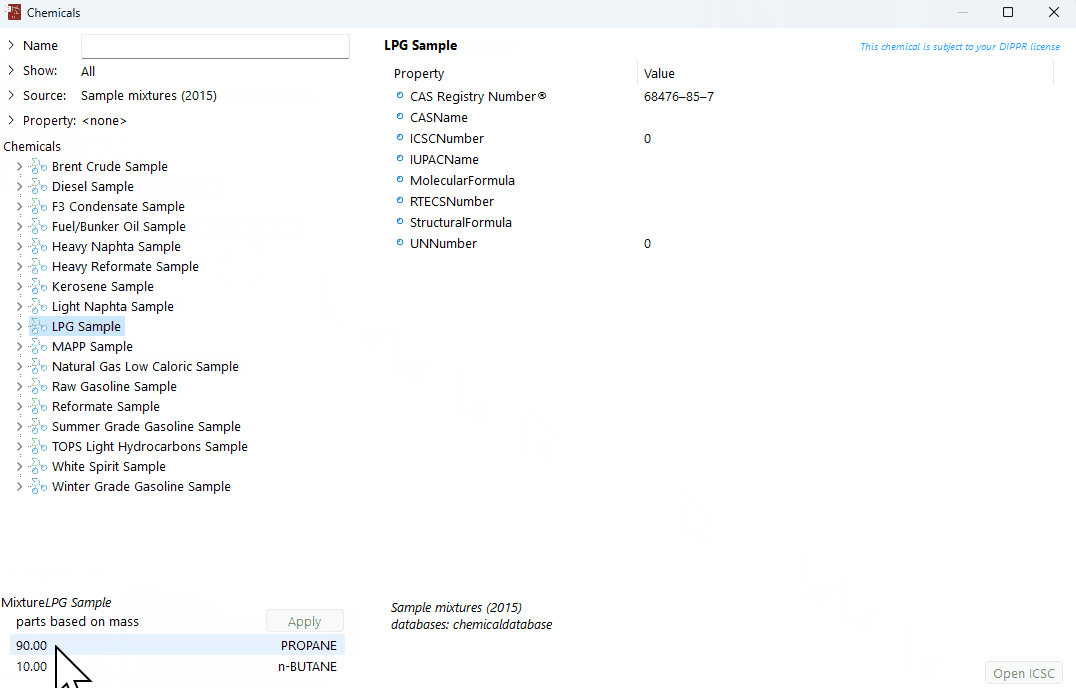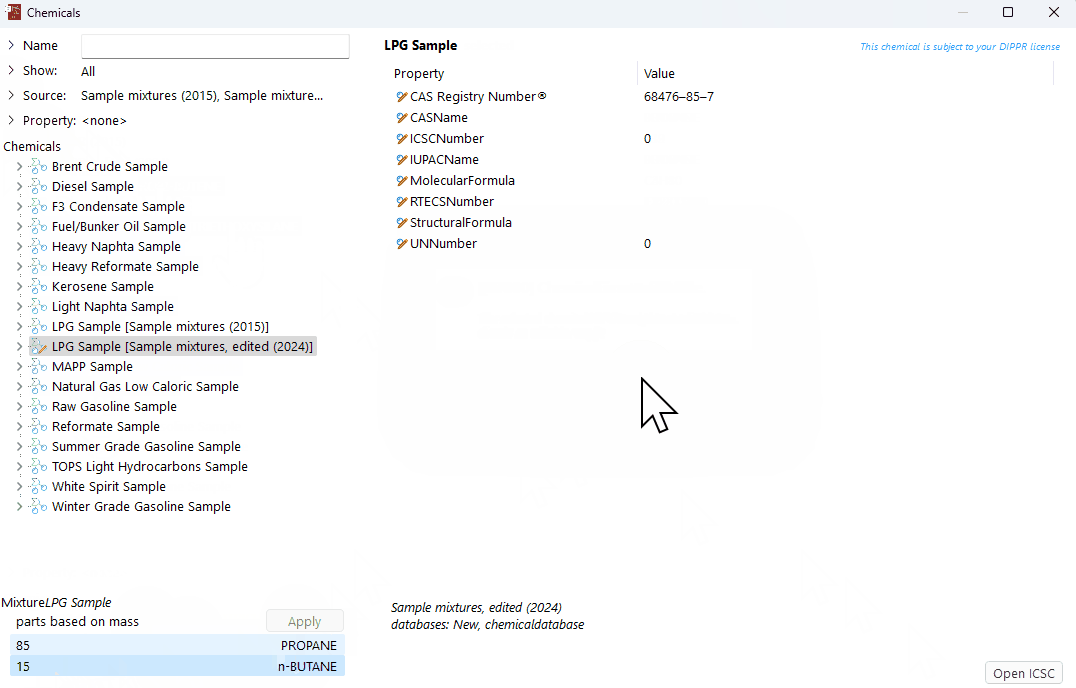
Click on the arrow next to "Source" in the chemical database window.
Deselect all the other chemical database sources, leaving only "Sample mixtures" selected.
Select a mixture to edit
Identify the sample mixtures to edit and click on it.
The composition of the mixture will be displayed.
Edit the composition
Click on the chemical component to edit.
Click on its corresponding composition (note that units can be changed to "parts based on moles" or "parts based on mass" by doing right click on this parameter).
The selected component in the mixture and its composition will be highlighted in blue.
Double-click on the composition to change its value.
Click Enter or anywhere else on the screen to save the value.
Save the edited mixture
Click the "Apply" button.
A confirmation window will appear prompting the user to create an editable copy of the mixture.
Click "OK" to confirm and save the editable copy of the mixture.
Method 2: Creating a new mixture from scratch
The second way to create a new user-defined mixture is to create the mixture from scratch. To do this, follow the steps below.
Select the DIPPR Database
Ensure that the latest DIPPR chemical database has been selected in "Sources" as the chemical database source.
Add the first chemical component of the mixture
Find the first chemical component for the new mixture. Use methods as described in “How does the chemical database work”.
Add the chemical component to the mixture, this can be done in two ways.
Click on the chemical component and 'drag-and-drop' to the "Mixture" section in the bottom-left corner.
Right-click on the chemical component and select “Add to mixture”.
Define the parts based on mass or moles (to change between mass and moles, right-click on "parts based on mass/moles" and select the relevant option).
Add additional components
Find the next chemical component to be added to your mixture.
Add the chemical to the mixture using either of the methods as explained in the steps above.
Repeat until all components are added.
Save the new mixture
Once you have added all the chemical components to your mixture, click "Apply".
You will then be prompted to name your new mixture, type in the desired name, for traceability, and click "OK".
The new mixture will be saved in the user-defined chemical database and will appear in the list of 'Chemicals' with the saved name, provided the user defined chemical database is selected as a source.
All new user-defined mixtures will be preceded by an orange bullet in the molecule logo next to the mixture's name.
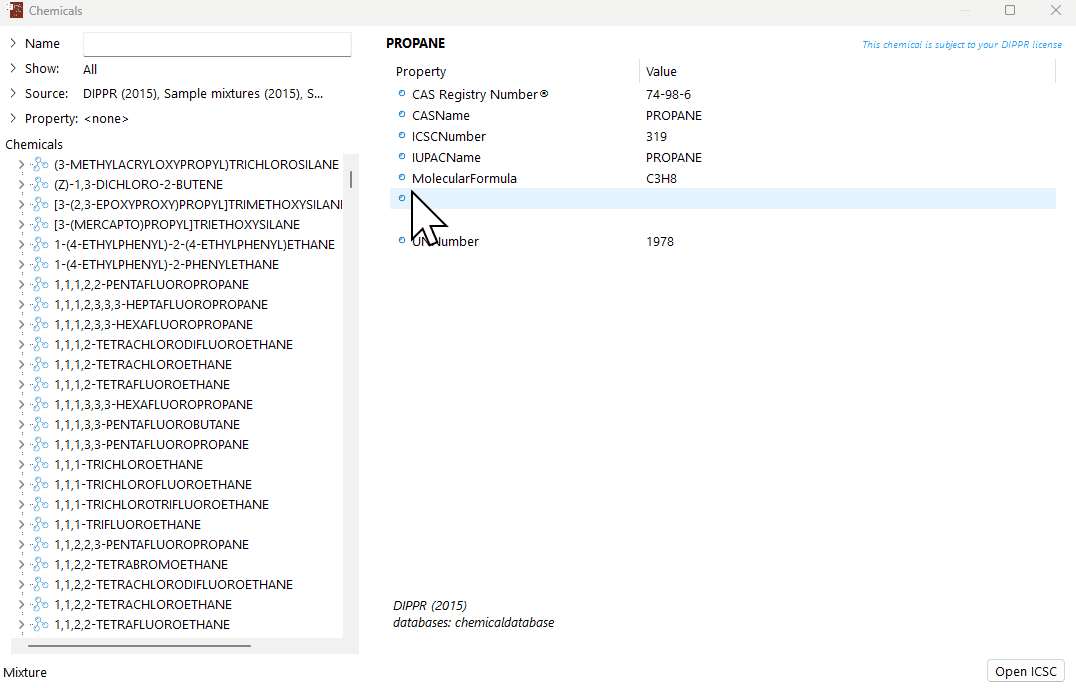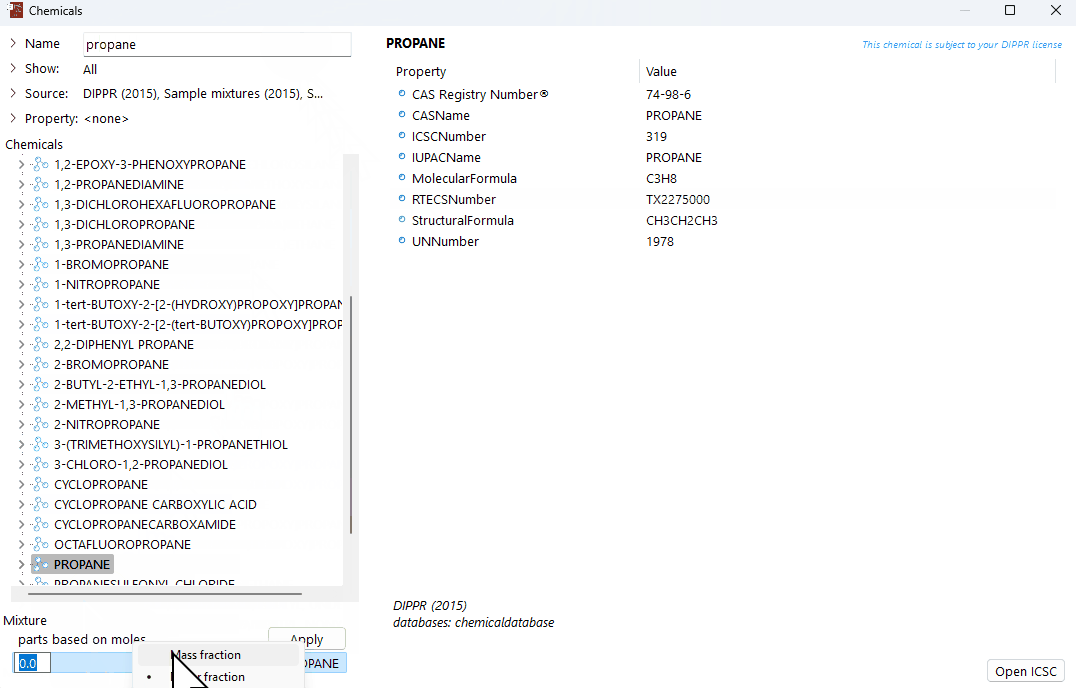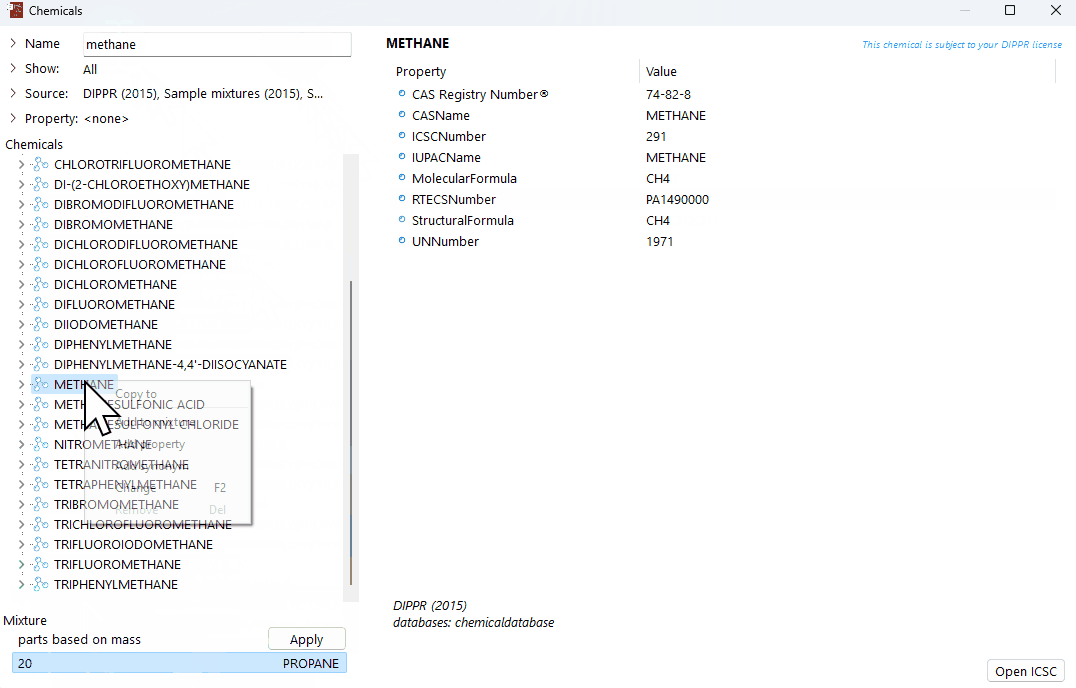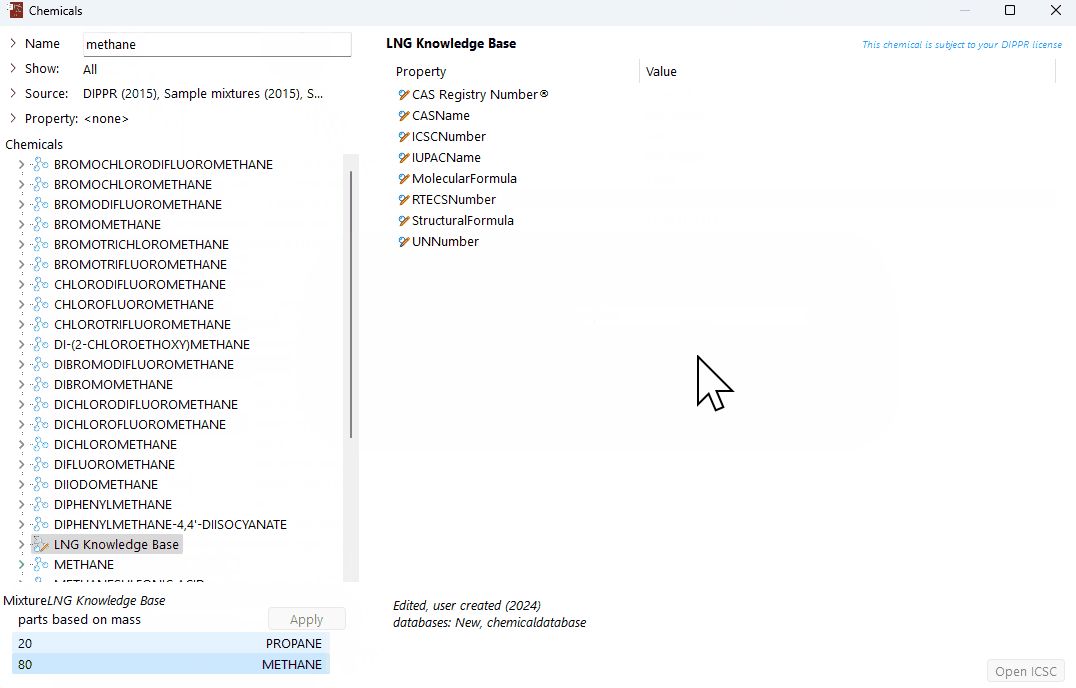
A demonstration of how to create a new mixture from scratch in the chemical database.
Conclusion
Creating mixtures within the chemical database in EFFECTS and RISKCURVES is a flexible and user-friendly process. Whether modifying an existing sample mixture or creating a new one from scratch, the ability to customise chemical compositions ensures accurate and tailored data for specific industrial needs. This customisation enhances the precision of consequence assessments for various scenarios, making the user-defined chemical database an invaluable tool for detailed and specific analysis.

